Beliebt in Ihrer Branche










































































































































































































Top-Kategorien
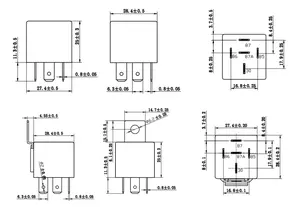
Über relais 2a 12v
Alibaba.com bietet hocheffiziente, leistungsstarke relais 2a 12v. die den Stromfluss innerhalb eines einzigen Stromkreises steuern. Die zuverlässigen Schalter an den Geräten können den Stromfluss auf sichere Weise beenden oder fortsetzen. relais 2a 12v. werden unter Verwendung hochwertiger Rohstoffe mit fortschrittlicher Technologie hergestellt. Sie sind für den dauerhaften Gebrauch ausgelegt und gewährleisten Haltbarkeit und optimale Leistung. Sie werden von zertifizierten Lieferanten zu fairen Marktpreisen mit fairen Angeboten verkauft.
relais 2a 12v sind wichtige Elemente des Elektrizitätssystems und müssen daher sehr gut gepflegt werden. Die auf Alibaba.com verfügbaren Relais befinden sich im Halbleiter und sind mit unterschiedlichen Kontaktlastkapazitäten kompatibel. Sie können sowohl im gewerblichen als auch im privaten Bereich eingesetzt werden, da das Risiko eines Schocks äußerst gering ist. Die Produkte sind in verschiedenen Größen erhältlich, um unterschiedliche Kontakte aufzunehmen.
Jedes Produkt ist auf überlegene Leistung ausgelegt und gewährleistet ein reibungsloses Funktionieren. Ein umfassender Katalog mit detaillierten Informationen zu jedem Produkt steht den Käufern zur Verfügung. Die Käufer können zwischen automatischen und elektrischen Relais sowie zwischen niedrigen und hohen Leistungseinstellungen wählen. Sie sind mit ISO- und CE-Zertifizierungen ausgestattet, um sicherzustellen, dass sie stoßfest und hitzebeständig sind. Das relais 2a 12v. Es gibt verschiedene Farben und Logos.
Stöbern Sie in der großen Kollektion, die exklusiv auf Alibaba.com zu erschwinglichen Preisen erhältlich ist. Diese klugen relais 2a 12v. Benutzer können den Stromfluss in allen Räumen einer Residenz problemlos steuern. Bei Lieferanten auf der ganzen Welt ist das Angebot endlos.