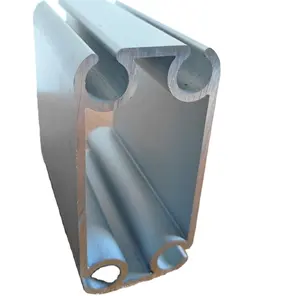
Achetez dès aujourd'hui pour des produits spectaculaires. profil en aluminium de catégorie sur Alibaba.com et découvrez des possibilités illimitées dans votre construction et d'autres applications. Le. Les profil en aluminium de catégorie sont disponibles dans toutes sortes de modèles et de tailles pour garantir leur application dans divers domaines. Outre leur robustesse et leur durabilité, les. Les profil en aluminium de catégorie sont très populaires en raison de leurs qualités remarquables qui ne peuvent être comparées à d'autres matériaux.
profil en aluminium de catégorie se vante de la meilleure durabilité environnementale par rapport aux matériaux qui ont le même objectif. L'aluminium est donc hautement recyclable. profil en aluminium de catégorie promouvoir la durabilité et la conception de bâtiments plus écologiques. Les propriétés réfléchissantes de l'aluminium en font une option idéale pour garder les bâtiments plus frais pendant les mois chauds. Bâtiments qui utilisent. profil en aluminium de catégorie nécessitent moins d'électricité pour la climatisation. Ceci est avantageux car cela permet d'économiser sur les factures d'électricité.
Tous. profil en aluminium de catégorie sur Alibaba.com offrent une résistance qui les rend hautement résistants aux intempéries. Quand le. profil en aluminium de catégorie sont utilisés dans diverses structures, ils ont la robustesse adéquate pour supporter les vitres lourdes nécessaires à l'éclairage naturel. Ils ont de la flexibilité. profil en aluminium de catégorie qui leur permet d'être courbés et extrudés en diverses formes qui ont des applications dans les secteurs de la construction.
Profitez d'innombrables avantages lorsque vous magasinez sur Alibaba.com. Découvrez sensationnel. profil en aluminium de catégorie propose aujourd'hui sur le site et choisissez celle qui vous convient le mieux. Vous en aurez pour votre argent tout en économisant du temps et de l'argent pour obtenir des articles de qualité. Utilisez les offres et les réductions sur divers. profil en aluminium de catégorie via les grossistes et les fournisseurs et obtenez ainsi les produits dans les limites de votre budget.































 浙公网安备 33010002000092号
浙公网安备 33010002000092号 浙B2-20120091-4
浙B2-20120091-4